ERP System in a nutshell
The ERP system as we know it today is a product of various factors and events that shaped its development.
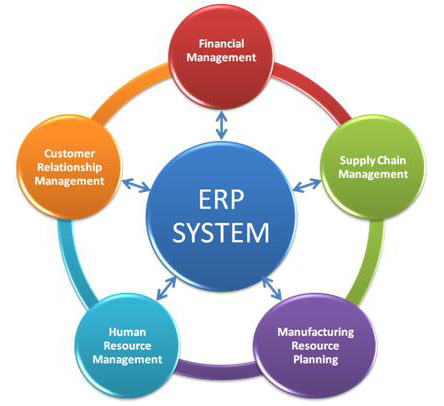
ERP stands for enterprise resource planning. As the name suggests, it covers the entire enterprise, not just aspects, or phases, or stages of the business operation.
An ERP system thus is something that encompasses the business from beginning to end.
Businesses, especially the bigger ones, have numerous and more complicated processes that not only need automation, but integration. An ERP system becomes vital in keeping track of information from every stage, as well as combing these different sets of information in order to tell a business story.
The ERP system has been described by many businesses as their backbone, their nerve center, without which the information would simply be isolated and meaningless data.
ERP System traces its roots to the manufacturing sector even though not all ERPs were developed from a manufacturing origin. Depending on specific business requirements, developers started with accounting, or maintenance, or human resources components. By the mid-1990s, the standard ERP system had covered all of the core functions of a business enterprise in any given industry.
Aside from private corporations, government agencies and non-profit organizations also started using their own ERP systems.
The year 2000 problem, when companies, industries and entire countries worried about the possibility data disruption by the so-called Y2K bug, acted as a catalyst for further developments and increasing popularity of the ERP software system. The adoption of a single currency in Europe was also another factor. Companies wanted to back up their entire systems just in case either of these two events cause them to lose vital company information.
In the beginning, core business functions or so-called back-office transactions were the focus of ERP system development. These were aspects of the operation that were internal to the business, i.e., those that did not deal directly with customers or the general public.
The advent of the internet however brought new challenges as well as opportunities. With data becoming more accessible to more people around the globe, front-office functions – those that dealt with the public – became popular. Terms such as customer relationship management, e-business and supplier relationship management emerged, highlighting the necessity of business to manage its communication with external parties. This became part of the evolution of the ERP system.
Companies with large, multi-region or multi-country operations find that they could employ the ERP system on two levels. There is of course one on the internal corporate side. The second level, again owing to the increasing popularity of the Internet, is a Web-based ERP system that allows corporations to integrate information from its subsidiaries and other branches and allows for real-time appreciation and analysis of consolidated data.
The realities of globalization and the possibilities offered by the Internet are factors determining the direction of ERP systems worldwide.
Need Help with ERP Implentation in the Philippines? Let’s Talk!
For a better understanding on what’s the best ERP Software for your organization, we could set a meeting so you could see its core features. A demo will let you see the software in action for you to be able to assess its critical features, price and the system’s ease of use.